Osteochondrosis is a common pathology of the spine, characterized by dystrophic changes in the structure of the vertebral cartilaginus disc and their bone base.
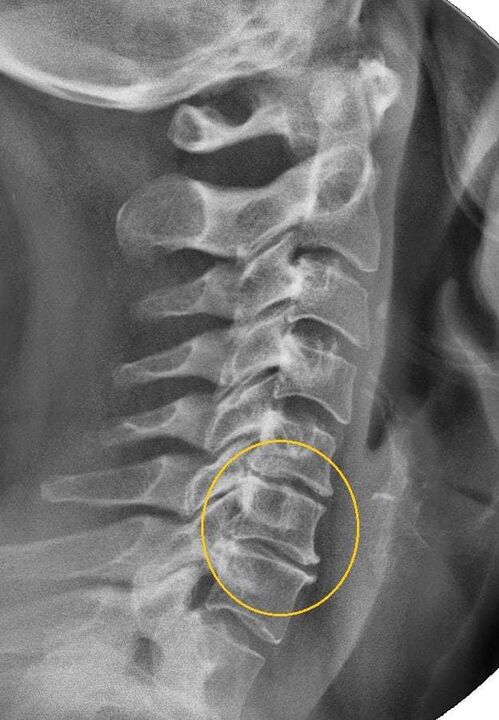
For one degree or another, osteochondrosis shows itself in most people after 30 years. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are diverse, which often complicates the diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
The cause of cervical osteochondrosis
Partly in the development of "guilty" neck osteochondrosis, frustrated with modern people and the same load distribution throughout the spinal column, as well as the natural processes of body tissue aging, in addition, there are some provoking the development and development of this pathology:
- SEDENTARI LIFE;
- Long stay in the same position while working;
- excess weight;
- continuous injury of the spine in the neck;
- chronic stress, persistent nervous tension;
- Normal hypothermia of the collar zone muscles (for example, when it is near air flow from air conditioning);
- Congenital vertebral anomalies and intervertebral discs.
General symptoms and signs of cervical osteochondrosis
The osteochondrous process affects any spine or some at once. Lumbar and cervical vertebrae are most affected by the pathology, as they are most vulnerable to the burden of the anatomy of the human skeleton.
The result of spinal osteochondrosis in the cervical region causes the most difficulty and complications, as its neck is a rich area of neuromus highways, most of which feed the brain directly.
For this reason, clinical symptoms with cervical osteochondrosis are widely associated with brain area ischemia. In addition, the nerve root, which provides the sensitivity and activity of the motor and shoulder rope, when squeezing with the destroyed vertebrate can provide a variety of symptoms.
Signs of neck osteochondrosis depends on the body's system influenced by pathology:
- The blood circulation is disrupted by compression of the vertebral artery determines most complex symptoms of the brain.
- Root compression that leaves the vertebrate gives a picture of the peripheral nerve wound.
- Pining the spinal cord is associated with severe neurological pathology found in advanced cases.
Below, consider the general clinic of the cervical spinal osteochondrosis.
Pain in the back of the head, neck and collar
These are the most common symptoms. The localization of pain can be expanded, affecting the shoulders, the clavicle region, chest, turning into intense head migraines.
The nature of pain depends on the localization of the lesion and the severity of the pathology. Initially, the pain can be temporarily temporary, gradually becoming chronic, painful.
At times of severity, pain becomes shooting, with increased neck muscle tone and limited head movements.
Often, pain with cervical osteochondrosis can be localized to the back of the sternum, where many patients take these symptoms for angina pectoris. Differentiation can be done by taking nitroglycerin pills - pain from osteochondrosis, they are not removed.
Noise, ringing, sensation of congestion in the ear
These symptoms often participate in hearing loss. This phenomenon is associated with a decrease in blood flow from the vertebral artery to the vestibular device.
Complex symptoms -these symptoms are called cochlear syndrome, or snails, and are far from always possible to determine their contact with osteochondrosis in the cervical region.
Special features for differentiation are noise, congestion and ringing in the ear when changing positions, after a long stay in one position.
Dizzy
Dizziness is also caused by a violation of blood flow to the inner ear organs, which ensures the body's balance. Nystagm often joins dizziness - fluctuations in the eyes to the eyes.
Shortage
This sensation arises due to irritation of the diaphragm nerves. It is a component of the cervical nerve beam and is involved in the regulation of respiratory, depth and frequency. The patient complains about the inability to breathe in the full chest.
In some cases, symptoms exacerbate shortness of breath and drowning. For the same reason, breathing stops at night and snoring.
Oxygen weakness due to respiratory problems eventually leads to increased fatigue, decreased concentration and memory problems.
Nausea
It is accompanied by air. It is also caused by problems with blood circulation in some areas of the brain and ears. Nausea is sometimes observed with vomiting -prostrated by head and body movements. The result of frequent nausea and vomiting is a decrease in appetite, weight loss, alimentary failure.
Problems with vision
"Flies" in the eyes, decreased visual acuity, fog in front of the eyes - these are all symptoms caused by the ischemia of the brain area responsible for vision.
Patients with osteochondrosis complain of lack of vision, as the lack of blood supply from the vertebral vessels is compensated by blood flow from the carbon artery system.
Glasses and therapeutic gymnastics for the eye muscles do not solve the problem, usually the vision improves after the treatment of osteochondrosis.
Blood pressure board
The unstable level of pressure is due to the affected blood flow in the oval brain responsible for the vascular-motor central function.
Suddenly -the fainting, or a syncopal state
It occurs with brain artery cramps as it stops short -term blood flow along the vertebral artery.
From the patient's loss of consciousness, you can quickly be removed by placing it so that the feet are slightly higher than the head - blood flow to the brain allows one to lead to life.
After fainting attacks, problems that can be reversed with speech and movement, due to short blood flow stops, can be observed for some time.

Symptoms of green
Often it may be the only sign that shows cervical osteochondrosis. They are expressed as sweat, dryness and lumps in the throat, difficulty with swallowing. Symptoms are associated with compression of the nerve plexus responsible for the conservation of faring. It is necessary to distinguish such manifestations from the same clinic for inflammation or neoplasms.
Increases body temperature
The increase in body temperature for cervical osteochondrosis is not the most typical, rare and localized symptoms: in the cervical and collar area, with a slight redness of the skin.
The osteochondrosis clinic in the cervical spine can, first, from various levels of severity, depends on the level of pathological development, as well as during their severity, and second, to form specific syndrome.
Symptoms depend on the level of cervical osteochondrosis
Level i
The beginning of the degenerative process in the cartilage of the vertebral disc. Symptoms are weak, sometimes they cannot be observed at all. The first signs of cervical spinal osteochondrosis:
- discomfort in the neck, arms, shoulders, sometimes turning into pain;
- headache;
- simple restrictions on neck motor activity;
- Quickly pass through the visual deterioration;
- Reduces the skin sensitivity of the collar area.
Important: These symptoms become clearer when tilted the head.
As a rule, in the first stage of osteochondrosis of the cervical area, the patient does not go to the doctor, believing that all symptoms are associated with fatigue, stress, age, lack of sleep.
Stage II
At this stage, the highlight of the vertebrate begins, the intervertebral cracks are narrow, the collagen fiber fiber of the disc is destroyed. There are symptoms that are painful from the point of the point of compression of the nerve stem, increasing during neck movement and head turn. Here you can already suspect cervical osteochondrosis, the second stage symptoms are as follows:
- Called pain in the neck, sometimes with problems;
- Shoulder and hand skin loss is almost entirely sensitive;
- Headache is frequent, do not pass for a long time;
- Visual deterioration with "flies" in the eyes;
- ring and noise in the ear;
- upper leg muscle weakness;
- The clarity of the tendon reflex reduced;
- shooting pain with dedication under the shoulder blade;
- Feelings of bumps in the throat, problems with swallowing;
- Sleep disorders, usually insomnia.
Long holding the head in one position leads to severe pain. At the developmental stage of the disease, the patient has come to the doctor for help.
Level III

The fibrous ring in the disc is destroyed, the hernia is formed. In the third stage, there are spinal deformation, displacement and vertebral dislocation due to their weak setting. Symptoms are as follows:
- pain, acute pain in the neck, collar zone, heart area;
- The sensitivity of the scalp in the back of the head, in the shoulder region, in the hands, until the absence of a complete;
- cervical spinal hernia;
- paresis and upper foot paralysis;
- Practical tendular reflexes are not observed.
This is a severe stage of the disease where the patient can no longer support his own head. Spinal cord ischemia and compression of the spinal artery lead to paralysis and paresis in other parts of the body and spinal stroke.
Syndrome caused by cervical spinal osteochondrosis
Not specific and a large number of symptoms accompanying cervical spinal osteochondrosis make it difficult to diagnose and further treatment, as some can be a completely different sign of disease. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are formed in a particular group called syndrome. Their presence and severity may indicate pathology in the cervical spine with updated localization.
A group of often found syndrome:
Korshka. Otherwise, it is called cervical radiculitis. It combines symptoms associated with cervical vertebral nerve root violations. "Goosebumps" in the affected area, tingling in the fingers, lower arms, skin skin, spreading to certain fingers are characteristic.
Irrititive-Reflex. The burning and acute pain in the back of the head and neck, sometimes with the return on the chest and shoulders, which occurs at the change in head and neck position, during sneezing, coughing and sharp head turn.
Vertebral artery syndrome includes:
- headache, attack or always, pulsating in nature;
- discomfort in several movements, including after long static position;
- weakness, nausea, loss of consciousness;
- Reducing hearing, problems with balance;
- Reduces visual acuity.
Heart. Almost the same picture as angina pectoris often leads to improper diagnosis and treatment. This syndrome arises due to irritation of the diaphragm nerve receptor, partly capturing the pericardium and large chest muscles. Thus, cramps in the heart region are more reflex, as a review of the cervical nerve irritation. Symptoms:
- Suddenly, prolonged pain, increased with neck movement, cough, sneezing, not passing when taking heart drug.
- ECG does not show blood flow from the heart muscle.
- Sometimes there are extrasystole and tachycardia.
Vegetative-Siabolic syndrome. The first vertebra subluxus departs the cervical with displacement can lead to the development of vegeto-vascular dystonia. It is not a specific diagnosis of VVD, as it does not have the symptoms mentioned.
There may be signs of neurological, symptoms of impaired cerebral blood flow, intracranial pressure, muscle cramps.
As a result, the patient's complaints go down to dizziness, decrease in visual acuity, loss of consciousness, headache, nausea.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis
The spinal cord described is a very serious pathology, which, by neglect, leading to defects, and the consequences of deep disruption of the cerebral circulation - and death. For this reason, with self -medication, if the symptoms appear, you cannot do it.
Osteochondrosis is treated in hospitals and at home exclusively as a doctor's prescription.
In the early stages, cervical osteochondrosis treatment was conservative, including prescription drugs: anti -inflammatory drugs, anesthetics, hormone medications, vitamin complexes, chondroprotectors -All of these relieves inflammation, pain.
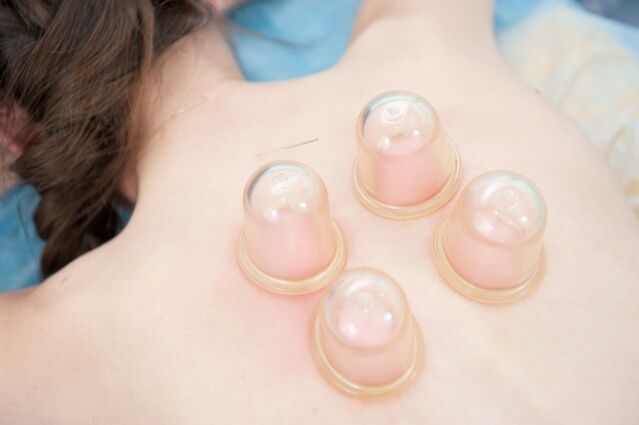
During the acute period, medications are prescribed in the form of injections, when the pain decreases, the patient goes to the tablet. Physiotherapy, massage, training training, usually prescribed at the remission level, participating in drug courses. In difficult cases, osteochondrosis is treated with surgery.
Prevention
The cervical spine health basis is a strong and healthy physical activity, a comfortable bed with anatomical pillows and mattresses, proper posture and proper nutrition.
Need to prevent neck injury and weight loss. It is necessary to incorporate prolonged sitting with a rest and warm time.
The forecast of recovery
Prognosis for qualified and timely treatment is good, but much depends on the age of the patient, severity of manifestations and levels of disease. It is also important where the person does medical advice on nutrition, lifestyle, and eliminating bad habits.
Conclusion
Therefore, in most cases, the cervical area osteochondrosis can be cured. However, keep in mind that the disease can return at any time. To avoid this, it is necessary to observe the precautionary measures and a healthy lifestyle.
In addition, keep in mind:
- The cause of osteochondrosis is difficult to establish.
- The symptoms of the disease are pain in the back of the head and neck.
- Cervical osteochondrosis is treated comprehensively: medicines (especially NSAIDs), massage, exercise therapy.























